Для сантэхнічных сістэм разуменне кампанентаў трубаправодаў мае вырашальнае значэнне для правільнай ўстаноўкі і эксплуатацыі, бо невыкананне гэтага патрабавання можа прывесці да ўцечак. Фітынгі NPT з'яўляюцца адным з найбольш распаўсюджаных тыпаў фітынгаў у сантэхнічных сістэмах. ДНЯЗ азначае Нацыянальны канус трубГэта стандартызаваная сістэма (ANSI B1.20.1), якая шырока выкарыстоўваецца ў Паўночнай Амерыцы для разьбовых злучэнняў паміж трубамі і фітынгамі. У гэтым артыкуле падрабязна разгледзім, што такое фітынгі для труб NPT і разьба NPT, як дакладна вымераць фітынгі NPT, каб дапамагчы вам выбраць правільныя фітынгі NPT.
Што такое фітынг для труб NPT?
Ан фітынг NPT — гэта разьбовае злучэнне, якое выкарыстоўваецца ў сантэхнічных сістэмах для стварэння герметычнасці паміж двума трубамі або паміж трубой і фітынгам. Разьба NPT звужаецца да асновы фітынга. Гэтая канічная форма стварае больш шчыльнае ўшчыльненне пры накручванні фітынга. Для забеспячэння герметычнага злучэння разьба NPT абапіраецца на герметык, напрыклад, герметык для труб або тэфлонавую стужку.
Яны ідэальна падыходзяць для агрэсіўных асяроддзяў, такіх як марская або хімічная апрацоўка. Звычайныя матэрыялы для разьбовых фітынгаў NPT ўключаюць латунь, вугляродзістую сталь і нержавеючую сталь.

Што такое разьба NPT?
Разьба NPT мае канічны дызайн, гэта можа забяспечыць моцнае механічнае злучэнне паміж трубамі і фітынгамі. Па меры таго, як вонкавая і ўнутраная разьба зкручваюцца разам, канічнасць стварае больш шчыльнае ўшчыльненне, што дапамагае прадухіліць уцечкі, асабліва пры выкарыстанні з адпаведным герметыкам для разьбы, такім як тэфлонавая стужка або герметык для труб. Такім чынам, ён можа вытрымліваць высокі ціск. У асноўным выкарыстоўваецца ў сантэхніцы і іншых сферах прымянення, звязаных з патокам вадкасцей.

Што такое кут разьбы NPT?
Стандарт разьбы NPT вызначае разьба пад вуглом 60 градусаў кут і пэўны крок, які ўяўляе сабой адлегласць паміж разьбой. Крок — гэта адлегласць паміж разьбой. Разьба распрацавана такім чынам, каб быць сумяшчальнай з іншымі фітынгамі NPT, што забяспечвае іх лёгкае падключэнне і адключэнне па меры неабходнасці. Звярніце ўвагу, што фітынгі NPT нельга падключаць да ўсіх фітынгаў. Трубныя фітынгі NPT прызначаны для канічнай трубной разьбы.

Ці могуць фітынгі NPT дасягнуць герметычнага злучэння?
Ушчыльненне разьбы NPT ажыццяўляецца праз механічнае злучэнне дзякуючы канічнай канструкцыі. Такая канічная форма стварае больш шчыльнае ўшчыльненне пры накручванні фітынга. Па меры таго, як вонкавая і ўнутраная разьбы зкручваюцца разам, канічная форма стварае больш шчыльнае ўшчыльненне, дапамагаючы прадухіліць уцечкі.
Прымяненне фітынгаў для труб NPT
Прамысловыя працэсы: фітынгі NPT выкарыстоўваюцца ў прамысловасці для перадачы вадкасцей і газаў пад ціскам. Яны выкарыстоўваюцца ў вытворчасці, хімічнай вытворчасці і нафтагазавай прамысловасці, дзе важныя надзейныя злучэнні.
Аўтамабільнае прымяненне: У аўтамабільнай прамысловасці фітынгі NPT выкарыстоўваюцца для паліўных і алейных трубаправодаў, дзе іх надзейнае злучэнне прадухіляе ўцечкі і забяспечвае аптымальную прадукцыйнасць.
Сантэхнічныя сістэмы: фітынгі NPT выкарыстоўваюцца для злучэння труб і арматуры. Яны ствараюць герметычнае ўшчыльненне, якое неабходна для падтрымання трубаправодных сістэм.
Сістэмы ацяплення, вентыляцыі і кандыцыянавання паветра: фітынгі NPT часта выкарыстоўваюцца ў сістэмах ацяплення, вентыляцыі і кандыцыянавання паветра (HVAC). Яны дапамагаюць злучаць розныя кампаненты, забяспечваючы эфектыўны кантроль паветранага патоку і тэмпературы.
Сістэмы пажаратушэння: надзейнасць фітынгаў NPT робіць іх прыдатнымі для сістэм пажаратушэння, дзе падача вады або хімічных рэчываў павінна быць пастаяннай і надзейнай.
Недахопы фітынгаў NPT
Схільны да пашырэння або расколін у адтуліне з-за празмернага зацягвання
Неабходная змазка для разьбы можа прывесці да забруджвання сістэмы
Як вымераць фітынгі NPT?
Дакладнае вымярэнне фітынгаў NPT вельмі важна для таго, каб яны правільна падышлі да вашай трубаправоднай сістэмы. Вось крокі для вымярэння фітынгаў NPT:
Як вымераць разьбу NPT
Вымярэнне разьбы NPT дазваляе вызначыць, ці з'яўляецца гэта фітынгам NPT. Па-першае, па вонкавым выглядзе NPT мае канічную разьбу, якая паступова патаўшчаецца, а не прамую цыліндрычную разьбу. Па-другое, трэба пераканацца, што гэта разьба з вуглом 60° (NPT — 60°, BSP — 55°).
Вызначце тып злучэння NPT
На выбар ёсць мужчынскае і ўнутранае злучэнне. Знешняе злучэнне NPT павінна мець памеры самой разьбы. Унутранае злучэнне NPT павінна мець памеры найбольшага дыяметра (верхняга дыяметра) разьбы.
Вызначце памер фітынга
Памер NPT заснаваны на ўнутраным дыяметры (ID) трубы, які з'яўляецца эфектыўным дыяметрам патоку, праз які праходзіць паветра, вада або іншыя вадкасці.
Фітынгі NPT звычайна ідэнтыфікуюцца па намінальным памеры, які адпавядае ўнутранаму дыяметру трубы, для якой яны прызначаны. Распаўсюджаныя памеры ўключаюць 1/8″, 1/4″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″ і гэтак далей. Аднак фактычны вонкавы дыяметр фітынга будзе большым за намінальны памер з-за таўшчыні матэрыялу.
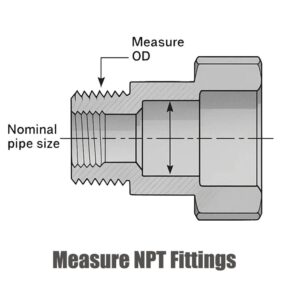
Вымерайце вонкавы дыяметр
Каб вымераць вонкавы дыяметр фітынга NPT, выкарыстоўвайце штангенцыркуль або рулетку. Размясціце вымяральны інструмент вакол самай шырокай часткі фітынга, пераканаўшыся, што вы вымяраеце вонкавы край разьбы. Запішыце гэта вымярэнне ў цалях або міліметрах.
The вонкавы дыяметр (OD) трубы большы чым намінальны памер з-за таўшчыня сценкі трубы, што дадае прыблізна 1/4 цалі (каля 1/16 цалі з кожнага боку).
Напрыклад, труба з надпісам 3/4 цалі NPT насамрэч мае вонкавы дыяметр каля 1 цалі, але намінальны памер адносіцца да ўнутранага дыяметра, дзе адбываецца паток
Вызначэнне кроку разьбы
Крок разьбы адносіцца да адлегласці паміж разьбой, і ён мае вырашальнае значэнне для вызначэння сумяшчальнасці фітынгаў для труб. Крок можна вымераць з дапамогай калібра або лінейкі. Падлічыце колькасць разьбы на пэўнай даўжыні (звычайна адзін цаля) і падзяліце яе на даўжыню, каб знайсці крок. Напрыклад, калі на адной цалі 11 разьбы, крок складае 11 разьб на цалю (TPI).
Вымерайце кут канічнасці
Хоць вымярэнне вугла канічнасці не заўсёды неабходнае, але яно дапамагае забяспечыць правільную пасадку. Стандартны вугал канічнасці для разьбы NPT складае 1 градус 47 хвілін (прыблізна 1,75 градуса). Пры неабходнасці можна выкарыстаць транспарцір для вымярэння вугла разьбы.
Табліца агульных памераў разьбы NPT
| Памер | ТПІ | Падача | OD | ID |
| 1/16 цалі | 27 | 0.941 | 7.895 | 7.142 |
| 1/8 цалі | 27 | 0.941 | 10.242 | 9.489 |
| 1/4 цалі | 18 | 1.411 | 13.616 | 12.487 |
| 3/8 цалі | 18 | 1.411 | 17.055 | 15.926 |
| 1/2 цалі | 14 | 1.814 | 21.223 | 19.772 |
| 3/4 цалі | 14 | 1.814 | 26.568 | 25.117 |
| 1 цаля | 11.5 | 2.209 | 33.228 | 31.461 |
| 1 1/4 цалі | 11.5 | 2.209 | 41.985 | 40.218 |
| 1 1/2 цалі | 11.5 | 2.209 | 48.054 | 46.287 |
| 2 цалі | 11.5 | 2.209 | 60.092 | 58.325 |
| 2 1/2 цалі | 8 | 3.175 | 72.699 | 70.159 |
| 3 цалі | 8 | 3.175 | 88.608 | 86.068 |
| 3 1/2 цалі | 8 | 3.175 | 101.316 | 98.776 |
| 4 цалі | 8 | 3.175 | 113.973 | 111.433 |
TPI = Колькасць разьб на цалю (1 цаля = 25,4 мм)
Вышыня тону = 25,4 ÷ TPI
АД = ID+2* Вышыня разьбы
Ідэнтыфікатар = Вышыня разьбы OD-2*
Праверце сумяшчальнасць
Пасля вымярэння вонкавага дыяметра, кроку і вугла канічнасці вы можаце параўнаць гэтыя вымярэнні са спецыфікацыямі фітынга, які плануеце выкарыстоўваць. Гэта дапаможа забяспечыць сумяшчальнасць фітынгаў і добрае ўшчыльненне пры злучэнні.
Для ўсіх, хто карыстаецца разьбовымі трубаправоднымі сістэмамі, вельмі важна разумець, як вымяраць памеры NPT. Выконваючы вышэйапісаныя дзеянні і звярнуўшыся да табліцы дыяметраў NPT, вы можаце пераканацца, што для вашага прымянення выбраны правільны памер разьбы, што прывядзе да бяспечнага і эфектыўнага злучэння. Правільнае вымярэнне прадухіляе ўцечкі і забяспечвае надзейнасць трубаправоднай сістэмы.