Because hydraulic systems operate under high pressure, hydraulic fittings must meet stringent design standards. Hydraulic fittings must be durable, reliable, robust, and corrosion-resistant. Therefore, they are typically made of high-resistance metals such as aluminum, brass, steel, and stainless steel. Different materials are suitable for different environments, but generally, fittings should be made of similar materials to the components they connect.
Hydraulic hose fittings all look the same, so how can you identify them?
Luckily, following the steps below makes it much easier than it seems.
Step 1: Reusable or Permanent?
Is the fitting reusable or permanent? Permanent fittings, or crimp fittings, are widely used in the fluid power industry because they are quick and easy to disassemble. They are also more reliable than reusable fittings.
Reusable fittings are easy to identify because they can be connected to the hose using only a wrench and a vise. However, reusable fittings are becoming less common because they are less reliable and more time-consuming to install.
Permanent fittings, on the other hand, are crimp-on and require a crimping tool.
Generally speaking, most fittings are permanent because they are more reliable and can be replaced more quickly.
Step 2: Identify the Fitting Ends and Port Connections
To ensure proper and safe assembly, it is important to identify the fitting with the correct port connection. There are many different types of port connections used in a wide range of applications. Use the following table to correctly identify the fitting end and port connection.
| Port Connections | Tube/Hose Connections | |
| NPT/NPTF | NPTF is a dry-sealing tapered pipe thread for fuel applications, suitable for both male and female fittings.
Although this connection is not recommended by the National Fluid Power Association (N.F.P.A.) for hydraulic systems, it is still widely used in fluid power systems. NPTF male threads will mate with NPTF, NPSF, or NPSM female threads. NPTF male fittings have tapered threads and a 30° internal cone. Female fittings have tapered threads but no internal cone. Sealing is achieved by thread engagement. NPSM has straight threads and a 30° internal cone. Sealing is achieved by the 30° cone. NPTF fittings are similar to BSPT fittings, but are not interchangeable. The thread pitch is different for most sizes. In addition, the NPTF thread angle is 60°, while the BSPT thread angle is 55°. NPSF threads are used for fuel applications, and sometimes a female end is used to mate with an NPTF male end. However, the SAE recommends using NPTF female threads with NPSF. NPSM is a straight pipe thread used for mechanical connections. This fitting is used for internally threaded swivel nuts in iron pipe swivel adapters. A tapered flat on the fitting end creates a leak-resistant connection, rather than a threaded connection. This connection is sometimes used in fluid power systems. |
37⁰ Flare |
| BSPT (JIS-PT) | BSPT male threads mate with BSPT female or BSPP female threads. BSPT male threads have tapered threads. When mated with BSPT female or BSPP female ports, sealing is achieved by interlocking deformation between the threads. Thread sealant is recommended.
BSPT fittings are similar to NPTF fittings but are not interchangeable. The thread pitch differs between the two on most sizes: BSPT threads have a 55° flare angle, while NPTF threads have a 60° flare angle. |
30⁰ Flare (Metric) |
| Metric Taper | 45⁰ Flare | |
| SAE Straight Thread | A metric straight pipe fitting consists of three accessories and a male threaded fitting body. These accessories are the steel pipe, the ferrule, and the ferrule nut. The assembly relationship of these three accessories is shown in the figure below. For DIN light series assembly, use DIN light series metric nuts. For DIN heavy series assembly, use DIN heavy series metric nuts. Select the ferrule and steel pipe according to the outer diameter of the steel pipe. | 24⁰ Flareless (SAE) |
| ISO 6149 | ISO 6149 is an international standard that specifies dimensions, design, and performance requirements for metric straight thread ports and fittings with an elastomeric O-ring for sealing. This standard is widely used in hydraulic systems in industrial and mobile applications, offering a robust and reliable solution for fluid power connections. | 24⁰ Flareless (DIN) |
| JIS-B2351 | British threaded JIS B2351 and Metric ISO 6149 both have O-ring elastomeric seals at the base of the threaded connection. Comparatively a tapered thread fitting simply seals with wedging of the metal-to-metal threads. Additionally, the O-ring seal in the JIS B2351 thread port provides good vibration resistance in construction and frequently actuated industrial machinery. They are also often used in the sealing port of Japanese hydraulic fitting studs. | 30⁰ Flare (BSPP) |
| DIN Metric | DIN Metric thread fittings, commonly used in Europe, are a type of hydraulic fitting characterized by a 24-degree cone and metric threads. These fittings are designed for connecting metric tubing to fitting threads, providing a secure connection even under high pressure and vibration. They are widely used in various industries, including oil & gas, construction, and automotive | O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) |
| BSPP (JIS-PF) | A universal British Standard thread, also known as a Whitworth thread. BSPP male fittings mate with BSPP female fittings or female ports. BSPP male fittings have straight threads and a 30° cone. BSPP female fittings have straight threads and a 30" cone. Female ports have straight threads and flats. Sealing on the port is accomplished with an O-ring or soft metal gasket on the male fitting. BSPP fittings are similar to NPSM fittings but are not interchangeable. The thread pitch differs on most sizes, with BSPP threads having a 55° angle compared to 60° for NPSM fittings. Female swivel BSPP fittings have a tapered protrusion that seals against the male thread's cone. | 60⁰ NPSM Swivel |
| 4-Bolt Flange | Commonly used in fluid power systems. Two pressure series are available: the first, designated 61, R-type, PN35/350 bar, representing the standard series; the second, designated 62, S-type, PN415 bar, representing the heavy-duty series or 6000 lb series. Both series share the same design concept, but the bolt hole spacing and flange head dimensions are larger in the 62 series. For four-bolt flanges, first measure the port hole diameter with a caliper. Then, measure the maximum bolt hole distance (dimension A) from center to center, or measure the flange head outside diameter. | 60⁰ Cone (BSPP) 60⁰ Cone (Metric) |
Step 3: Determine the Sealing Method
The type of hydraulic fitting depends on size, configuration, and thread type. O-ring, mated angle, and threaded fittings are the most common, but several other types of hydraulic hose fittings are available.
O-Ring: There are three types of O-ring seal designs: boss, flat, and flange. For these types of fittings, the O-ring is the primary component that creates the seal. Male O-ring threads mate only with female O-ring threads, which are typically used on oil ports.
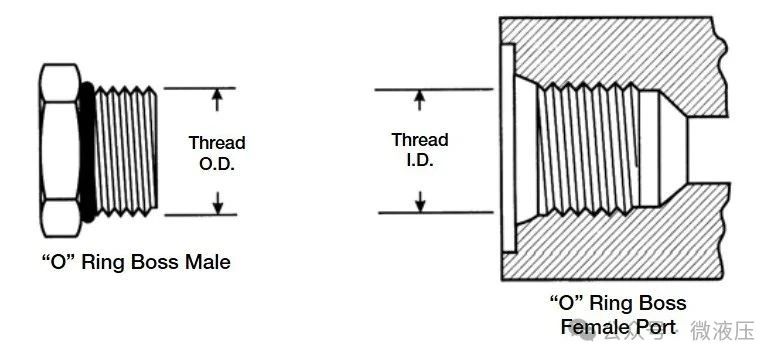
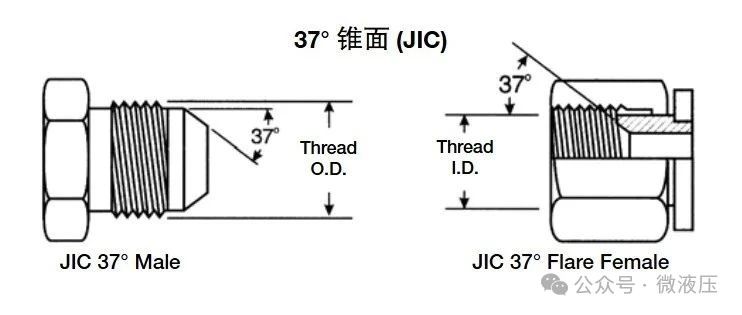
Mated Angle: SAE 45° or JIC 37° are examples of mating angles, but many more exist. Angle socket fittings use straight or parallel threads for sealing. When the male and female threads are threaded together, the threads do not create a seal. Instead, a seal is created when two mating angle sockets are connected. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) specifies a 37° flare or cone for sealing high-pressure hydraulic lines. This design is commonly referred to as a JC fitting. A JIC 37° external cone only mates with a 37° internal cone. JIC male threads are straight threads with a 37° cone. JIC female threads are straight threads with a 37° cone. Sealing is achieved by a line seal formed between the 37° internal and external cones. The threads create a mechanical connection.
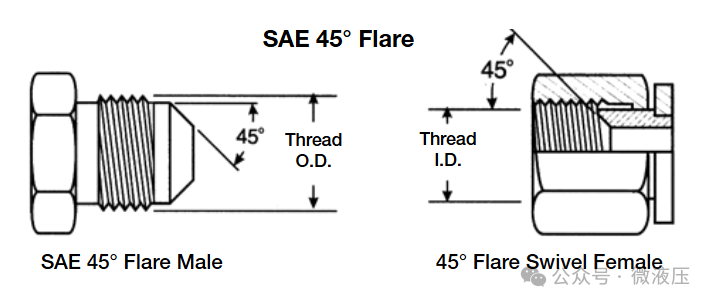
Tapered Threads: Tapered thread fittings come in two types: male and female. Male threads are on the outside of the fitting, while female threads are on the inside. When the two are screwed together, the tapered threads deform, applying pressure to the fitting and ultimately forming a seal. Tapered threads are generally not very precise, but tape should never be used to ensure a seal. This is usually suitable for fittings with a 45° flare or cone. This type of seal is often used with soft copper tubing, as it is easier to flare to a 45° angle. This is often used in low-pressure applications such as refrigerators, automobiles, and truck fittings. An SAE 45° external cone will only mate with an SAE 45° internal cone.
Step 4: Check the Fitting Design
Check the location of the O-ring, nose seat, seat angle, and fitting termination. You can see the O-ring location as well as the type of nose seat. A seat gauge is required to determine the seat angle.
| Mated Angle Seat with O-ring: | |||
| O-Ring Location | Nose Seat | Seat Angle | Fitting Termination |
| Inside | Inverted | 60⁰ Inclusive | British Standard Pipe Parallel |
| Inside | Inverted | 24⁰ Inclusive | DIN 24 ° Cone |
| O-Ring Face Seal: | |||
| O-Ring Location | Nose Seat | Seat Angle | Fitting Termination |
| In Flange Groove | Flat Face | N/A | SAE O-Ring Flange (Code 61 or 62) |
| Outside | Flat Face | N/A | SAE O-Ring Boss |
| At Nose Seat | Flat Face | N/A | O-Ring Face Seal |
| Mechanical Joint or Mated Angle: | |||
| O-Ring Location | Nose Seat | Seat Angle | Fitting Termination |
| None | Standard | 37° | JIC 37° Flare |
| None | Standard | 45° | JIC / SAE 45° Flare |
| None | Standard | 30° | Japanese Industrial Standard & Komatsu |
| None | Inverted | N/A | Metric Stand Pipe |
| None | Inverted | 30° | National Pipe Straight |
| None | Inverted | 45° | SAE Inverted Flare |
| None | Inverted | 24° | Inclusive French Gaz 24° Cone |
| None, except -20 | Standard | 24° | Inclusive French Gaz 24° High-Pressure Flange |
| Thread Interface: | |||
| O-Ring Location | Nose Seat | Seat Angle | Fitting Termination |
| N/A | N/A | N/A | National Pipe Tapered |
| N/A | N/A | N/A | British Standard Pipe Tapered |