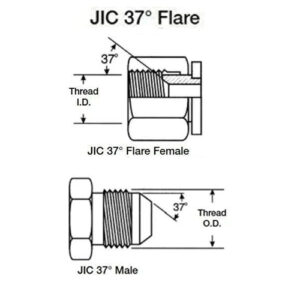
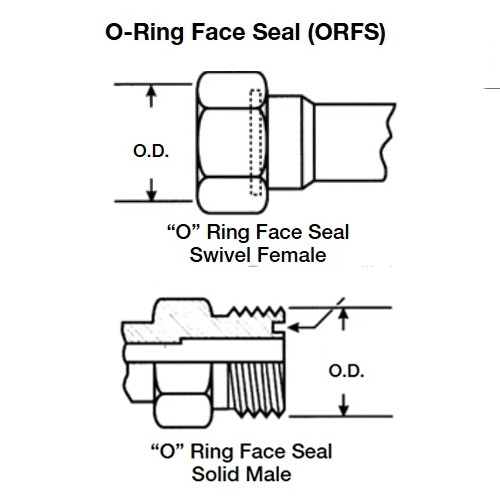
You might be surprised to learn that mismatched hydraulic hoses and fittings are one of the most common causes of leaks and hydraulic system failures. Improperly matched hoses and fittings can lead to leaks, inefficiencies, or catastrophic failure in hydraulic systems.
Even a minor mismatch in size or material compatibility can cause problems and impact the performance of the entire system. Therefore, matching the correct hose size and fitting type is crucial to maintaining system reliability.
Below, we'll provide a guide on how to proper size hydraulic hoses and fittings, helping you and your hydraulic system avoid another tragedy.

Hydraulic Hose
Hydraulic hoses are flexible hoses made of rubber, thermoplastic, or stainless steel, used to transport fluids within hydraulic systems. Hydraulic hoses are key components in hydraulic systems, playing a vital role in transmitting fluid power within mechanical equipment. They withstand high pressures and transport hydraulic fluid between various components, such as pumps, valves, cylinders, and motors.

What are hydraulic hose sizes?
Understanding hose size is the first step in correctly installing hoses and fittings and is key to designing and maintaining an efficient and safe hydraulic system.
Hydraulic hoses come in a variety of sizes to accommodate different fluid types, pressure levels, and flow requirements. Hydraulic hose size directly affects fluid flow, pressure rating, and overall system performance.
Selecting the wrong hose size can lead to inefficiencies, equipment damage, and even safety hazards.
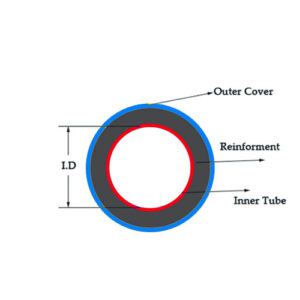
Hydraulic Hose Size Definition - Hose Inside Diameter
Hose size refers to the inside diameter of the hose, which determines the system's flow rate. It is typically measured in inches or millimeters.
Hose size is typically expressed by two primary measurements: the inside diameter (ID), which is the actual opening through which the fluid passes; and the outside diameter (OD), which is the overall size of the hose (including its reinforcement).
Selecting hose size is crucial because it affects not only the fluid flow rate but also the pressure rating and overall system efficiency.

How Hose Size Affects Fluid Flow and System Efficiency
Hose size is directly related to the flow rate of fluid in a system. Larger hoses allow for greater fluid flow, which is crucial for high-flow systems, while smaller hoses are suitable for lower flow rates. However, improper hose sizing (oversized or undersized) can lead to performance issues:
Too small: A hose with a small diameter creates resistance, causing frictional losses and reducing fluid flow. This can lead to pressure drops, overheating, inefficiency, and even damage to hydraulic components.
Too large: A hose that is too large can allow fluid to flow too easily, reducing the required pressure in the system, potentially causing hydraulic performance issues and inefficient energy use.
Ensuring the proper hose size helps maintain consistent flow rates, reduces energy consumption, and ensures that the system operates optimally without overworking the pump or causing unnecessary pressure fluctuations.
Common Hydraulic Hose Sizing Terminology
Understanding the terminology used in hydraulic hose sizing calculations helps ensure proper hose selection and installation. Some common terms include:
Inside Diameter (ID): The measurement of the fluid flowing inside a hose. It is one of the most critical factors in determining the amount of fluid a hose can transport.
Outside Diameter (OD): The external measurement of a hose, which is important for fitting compatibility and understanding how the hose fits into the system layout.
DASH Size: Most hoses have an inside diameter in 1/16-inch increments, for example: 1/2-inch → "-8" (8/16), 2-inch → "-32" (32/16).
Nominal Size: Nominal sizes are often used to simplify communication and refer to a general size designation for the hose (e.g., ½-inch, 1-inch), but they do not always represent the exact inside diameter.
Pressure Rating: The maximum pressure a hose can safely withstand. Hydraulic hoses have varying pressure ratings, and the pressure rating is typically related to the hose's size and material.
Reinforcement: A layer of material (such as steel or textile) within the hose that provides strength and support to withstand internal pressure and external forces.
Factors to Consider When Properly Sizing Hydraulic Hose
Choosing the correct hose size is crucial to the performance and safety of your hydraulic system. Several key factors influence this decision, from hose diameter to system design.
Hydraulic Hose Inside Diameter Size and Its Role in System Flow
Hydraulic hose diameter plays a significant role in determining system flow. The larger the hose's inside diameter (ID), the greater the amount of fluid it can flow. Diameter affects system performance as follows:
Flow rate: A larger hose diameter reduces fluid flow resistance, enabling higher flow rates. This is crucial for high-flow applications where efficient fluid flow is crucial.
Pressure drop: A hose diameter that is too small can result in significant pressure drop, reducing overall system efficiency. Fluid flow through a smaller hose faces greater resistance, leading to energy loss and potential overheating.
Friction loss: A smaller hose diameter increases frictional resistance, reducing system efficiency, resulting in higher operating costs and potential equipment stress.
In summary, the hose diameter must be selected based on the required flow rate and pressure to ensure smooth and efficient system operation.
Pressure Rating: Why It's Important for Hose Sizing
The pressure rating of a hydraulic hose is one of the key factors in selecting the correct hose size. It determines the maximum pressure the hose can safely withstand before failure. Pressure ratings vary depending on the hose's material, construction, and diameter. The importance of pressure ratings is demonstrated in the following ways:
Matching Pressure Requirements: Hydraulic systems operate at specific pressure levels. If the pressure exceeds the hose's rating, the hose may rupture, leading to fluid leakage, system damage, and safety risks. Ensuring that the hose's pressure rating matches the system requirements is crucial to avoid failures.
The Effect of Hose Diameter on Pressure: Hoses with larger diameters typically have lower pressure ratings than hoses with smaller diameters. This is because larger hoses typically have less reinforcement and expand more easily under high pressure. On the other hand, smaller hoses, due to their reinforced construction, can generally withstand higher pressures.
Safety Factor: Always select a hose with a pressure rating higher than the system's operating pressure to provide a safety margin and prevent failure in unexpected situations.

Fluid Type and Temperature: Impacting Hose Size and Material
The fluid type and temperature in a hydraulic system affect the material properties and size of the hose. Different fluids (such as water-based, oil-based, or synthetic fluids) interact differently with hose materials. Here's how these factors influence hose selection:
Fluid Compatibility: Certain hose materials are better suited for specific fluids. For example, a hose designed for petroleum-based fluids may not be compatible with water-based fluids, which can result in reduced hose performance. Selecting a hose with compatible material properties is crucial to ensuring long-term performance.
Temperature Range: Hydraulic systems typically operate within a wide temperature range, from very low to very high. Hoses must be able to withstand these extreme temperatures without damage. High temperatures can cause hoses to become brittle, leading to cracking, while low temperatures can make them stiffer and more susceptible to failure.
Viscosity and Flow Characteristics: Fluid type also affects viscosity, which in turn affects how easily the fluid flows through the hose. Fluids with higher viscosities require larger diameter hoses to reduce resistance and maintain adequate flow. At high temperatures, viscosity decreases, and hose size may need to be adjusted to prevent fluid flow issues.
Environmental Conditions and Their Impact on Hose Sizing
Environmental conditions such as UV rays, chemicals, abrasives, and extreme weather can significantly impact the performance and service life of hydraulic hoses. Consider the following environmental factors when selecting a hose:
UV exposure: Continuous exposure to sunlight can cause degradation of hose materials, especially rubber hoses. If your hydraulic system operates outdoors, be sure to select hoses with UV-resistant materials or coatings to prevent premature wear.
Chemical exposure: If your hydraulic system operates in an environment where the hose may come into contact with chemicals (such as oils, solvents, or acids), selecting a hose with appropriate chemical resistance is crucial. Some hose materials are more resistant to certain chemicals than others.
Abrasion and physical damage: In environments where the hose may come into contact with sharp objects, dirt, or abrasives, it's necessary to select a hose with higher abrasion resistance. Hoses designed for high-wear areas typically feature outer covers made of materials such as steel braid or tough rubber.
Extreme temperatures: Hoses used in extremely hot or cold environments must be carefully selected to ensure they can withstand temperature fluctuations without cracking, hardening, or losing flexibility. Thermoplastic hoses are ideal for extreme temperature environments.
Hydraulic System Design and Its Role in Selecting the Proper Hose Size
Overall system design is a key factor in selecting the appropriate hose size. The layout, fluid flow requirements, pressure conditions, and expected operating environment all influence the optimal hose size. Key system design considerations include:
Layout and Routing: The hose's path through the system affects its size and flexibility. Sharp bends and long routings may require a smaller diameter hose or special reinforcement to prevent kinking or damage.
Pressure and Flow Conditions: Hydraulic systems with higher pressure and flow requirements may require larger hoses or more advanced materials to handle the higher loads. Ensuring that the hose size matches the system's pressure and flow is crucial for achieving optimal performance.
Space Constraints: Systems with limited space may require a smaller diameter hose to meet design constraints. However, the smaller hose must still meet the system's flow and pressure requirements.
System Modularity: If the hydraulic system is modular and components are interchangeable, standardizing hose sizes across the system can simplify maintenance and repairs.
Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic hose fittings are essential components of any hydraulic system. They connect hydraulic hoses and pipes to other components, preventing leaks and ensuring the proper functioning of the entire system.
There are two basic types of hydraulic fittings: high-pressure fittings and low-pressure fittings. Both types of fittings come in a variety of shapes, such as elbows, tees, crosses, and straights.
These fittings are further categorized into single-ring fittings, double-ring fittings, push-on fittings, and push-on fittings.
Common materials for hydraulic fittings include aluminum, brass, stainless steel, and plastic.

Hydraulic Hose Fitting Connector Sizes
The hydraulic hose fitting size is determined by two main factors: the inside diameter (ID) of the hose it fits and the type of connector.
Hydraulic Hose Connector Fitting Inside Diameter (ID):
This refers to the size of the hose opening the connector is designed to connect to. It is typically expressed in inches (e.g., 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, 1/2 inch) or millimeters (e.g., 6 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm).
You can find this information on a hose size chart or directly on the hose itself.
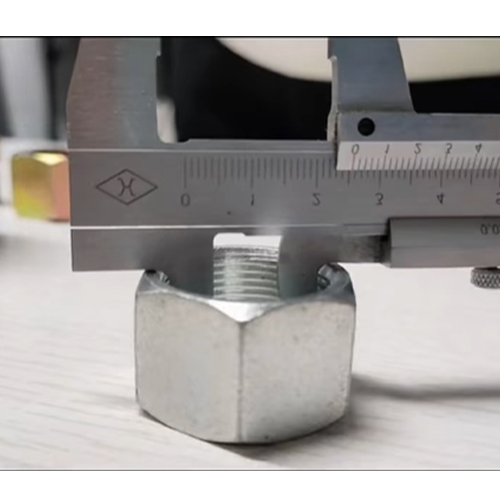
Factors to Consider When Sizing Hydraulic Fittings
Industrial hydraulic hose fittings are essential components for a variety of hydraulic systems. Understanding the different types of fittings, the materials they're made of, and their typical applications is crucial for selecting the right fitting for your specific needs.
Choosing the right fitting ensures your hydraulic system operates safely and efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
The most important factors to consider when selecting the right hydraulic hose fitting include size, material, temperature range, and pressure requirements.
You should also consider the application and the fitting's intended use, the type of hydraulic fluid, and its compatibility with the fitting.
Finally, if the fitting will be frequently connected and disconnected, you'll want to find one that's easy to assemble and disassemble.
Remember that two hydraulic fittings that appear identical may not necessarily be the same size—always check.
Steps to Properly Sizing Hydraulic Fittings
Follow these steps for accurate thread identification, inside and outside diameter (ID), or male/female measurements.
First, you need to understand what inside diameter and thread size are.
Inside diameter (ID): This refers to the hose size the fitting is intended for. For male fittings (external threads), use a caliper in OD mode; for female fittings (internal threads), use a caliper in ID mode.
Thread size: A caliper can only provide a rough measurement, but a thread gauge is ideal for precise measurement. The number of teeth on the thread gauge should match the size and type of thread (e.g., NPT 1/2-14).
1. Measuring Length
This can be easily measured with a simple tape measure. Place the fitting on a flat surface and measure with the tape measure.
2. Determining the Outside Diameter
The outside diameter, also known as the outside diameter of a male hydraulic fitting, can be measured with a vernier caliper. First, zero the caliper, then place the fitting between the parallel threads of the jaws, closing the jaws until they grip the fitting securely.
This method provides highly accurate readings. Remember the principle of "measuring twice"? Let's use this here to save you trouble later.
3. Measuring the Inside Diameter
The steps for measuring internal threads are similar to those for external threads. However, this time, insert the jaws of a vernier caliper into the fitting to obtain an accurate reading. As before, take two measurements to get an accurate result.
4. Calculating the Thread Size
The teeth of the pitch gauge determine the thread size. Place it over the thread you want to measure. Ensure the threads fit snugly, with no gaps between the fitting and the teeth. Then, visit the manufacturer's website or catalog to find a matching thread to ensure accurate measurements.
If you don't have a pitch gauge, you can use a vernier caliper again to estimate the diameter. For imperial and European threads, the thread gauge measures threads per inch, so simply calculate the number of threads per inch.
5. Determine the Angle
The angle of the fitting is very important. The most common angles for elbow fittings are 45° and 90°, but be sure to use a protractor to get an accurate measurement, as angles can vary.
How to Properly Select Hose and Fitting Sizes: A Step-by-Step Guide
When selecting the appropriate hose size for your system, it's important to follow a systematic approach. Matching the appropriate hose size with the fitting ensures optimal performance, safety, and system longevity.
Step 1: Determine the hydraulic system's fluid flow and pressure requirements
Before selecting a hose size, it's important to understand the system's flow and pressure requirements. The flow rate and system pressure determine the size and type of hose required for efficient operation without overloading components.
Fluid Flow: Determine the system's required flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM). Higher flow rates require larger hose diameters to ensure adequate fluid flow.
System Pressure: Determine the system's operating pressure (typically measured in PSI or bar). The hose's pressure rating should match the system's maximum pressure to prevent hose failure.
Peak Pressure: Consider peak pressures or pressure spikes that may occur during startup or load changes. The hose must withstand not only the typical operating pressure but also brief pressure fluctuations that may exceed normal levels.
Step 2: Choose the Right Hydraulic Hose Type for Your Application
Not all hoses are suitable for all applications, so it's crucial to choose the right hose material and type based on the fluid being conveyed and the environmental conditions. Here are some things to consider:
Fluid Type: Select a hose compatible with the system fluid, such as oil, water, chemicals, or air. Some hoses are specifically designed to withstand certain fluids, such as petroleum-based oils or water-based fluids.
Temperature Range: Select a hose that can withstand the fluid temperature and environmental conditions. High temperatures can cause the hose material to degrade, while low temperatures can make it brittle.
Environmental Factors: Consider external factors such as UV exposure, chemicals, abrasion, and mechanical stress. For example, hoses used outdoors or in harsh environments should be resistant to UV and chemicals.
Reinforcement: Some applications may require a reinforced hose to withstand high pressures or provide increased flexibility. Consider whether your system requires a braided, spiral, or fabric-reinforced hose.
Step 3: Select the Correct Hose Diameter Based on Pressure and Flow
Hose diameter directly impacts fluid flow and system efficiency. To select the correct diameter, use the following formulas and guidelines:
Flow Formula: Use flow rate and pressure drop (the pressure loss as the fluid flows through the hose) to determine the appropriate hose diameter. A common formula for flow in a pipe or hose is:
Flow Rate = Cross-sectional Area of Hose × Fluid Velocity
Note: The ideal flow rate should strike a balance between providing sufficient flow and preventing excessive pressure drop.
Pressure Considerations: If your system requires higher pressure, you will need a smaller diameter hose to maintain the appropriate pressure level. Conversely, an oversized hose will reduce system pressure and lead to inefficiencies.
Viscosity and Flow Resistance: If your fluid has a higher viscosity (such as oil-based fluids), you may need a larger diameter hose to reduce resistance and maintain the desired flow rate. For low-viscosity fluids (such as water), a smaller diameter hose can generally be used.
Nominal Size: The nominal size of a hose refers to its general size designation (e.g., ½ inch, 1 inch), but remember that the inside diameter (ID) is the key measurement for accurate sizing.
Step 4: Calculate the Proper Fitting Size and Match the Fitting Type and Size to the Hose
Now that you've determined the required hose diameter and selected the appropriate hose material and type, you need to focus on matching the fitting size to the hydraulic hose. This step ensures a proper connection between the hose and fitting, preventing leaks, pressure loss, and other system inefficiencies.
Here's how to calculate the correct fitting size:
Determine the hose's inside diameter (ID)
The hose's inside diameter (ID) is a critical dimension for matching with fittings. The ID directly affects fluid flow and pressure ratings. Ensure the fitting's ID matches or is slightly larger than the hose's ID to maintain smooth fluid flow and prevent clogging.
Determining Fitting Type and Size
Hydraulic fittings come in a variety of types and sizes, each designed for a specific hose type and application. Some common fitting types include:
BSP (British Standard Pipe) fittings
NPT (National Pipe Thread) fittings
JIC (Joint Industrial Committee) fittings
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) fittings
Metric fittings
The type and size of the fitting should match the hose size and system requirements. When selecting a fitting, be sure to understand the thread type (e.g., BSPP, NPTF) and connection method (e.g., flare, swivel, crimp).
Measuring the Fitting's Outside Diameter (OD)
For most fittings, the outside diameter (OD) is an important measurement to ensure a snug fit on the hose connector port. The fitting's OD should match the hose connector port size (this size may be determined by the system connection or valve port size).
Thread Compatibility: Ensure the fitting threads match the corresponding threads on the hose end or within the fitting system. Thread mismatches can cause leaks and pressure loss.
Fitting Length: The length of the fitting is important, especially for compression and crimp fittings. Longer fittings provide a more secure connection, while shorter fittings may be more suitable for systems with limited space.
Select the Correct Fitting Size Based on Hose Diameter
Once you've determined the correct hose diameter and material, you can match it to the appropriate fitting size. This fitting should have the following characteristics:
To ensure smooth fluid flow, the inside diameter should match or be slightly larger than the hose's inside diameter.
The outside diameter should be appropriate for the port or connection point in the system.
For example:
A 1/2-inch hose typically requires a 1/2-inch fitting or an appropriately sized fitting to ensure a tight and secure connection.
For smaller or larger hoses, ensure the fitting type and size match the hose's inside and outside diameters.
Conclusion
Optimizing hydraulic system performance begins with the correct selection and matching of hydraulic hoses and fittings. If you're having trouble selecting the right hose size for your existing fittings, contact Sinopulse and our experts will be happy to assist you in selecting the best option.
FAQ
What is Hose Sizing?
Hydraulic hose sizing refers to determining the correct hose diameter and type to meet the specific requirements of a hydraulic system. This is crucial because using the wrong hose size can lead to a variety of problems, including pressure loss, reduced efficiency, overheating, and even hose failure. An improperly sized hose cannot withstand the required flow and pressure, resulting in poor performance and potential damage to the equipment.
Hydraulic Hose Construction
Hydraulic hoses typically consist of three components: an inner tube, a reinforcement layer, and a cover. The inner tube transports the hydraulic fluid, the reinforcement layer provides the required strength and pressure resistance, and the cover protects the hose from the environment.
Why Choose the Correct Hose Size?
Properly sized hydraulic hoses offer many advantages. They minimize pressure loss and maximize flow, ensuring optimal system performance. This translates to increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and extended equipment life. Properly sized hoses also operate at lower temperatures, reducing the risk of overheating and hose failure. Choosing the right hose material for the fluid and environment can further improve durability and prevent leaks.
How to Determine Hydraulic Hose Size?
The size of a hydraulic hose depends on a variety of factors, including the required flow rate, operating pressure, fluid type, and hose length. Manufacturers provide charts and tables outlining recommended hose sizes based on these parameters. You also need to consider the application type, as different hoses are designed for specific environments and conditions. Factors such as temperature, abrasion resistance, and chemical compatibility can affect hose size.
How do you measure the diameter of a hydraulic hose?
There are two main methods for measuring the inside diameter of a hydraulic hose: using a vernier caliper or micrometer, and using a bore gauge or internal micrometer. Open the jaws of the vernier caliper or micrometer and gently insert them into the hose until they touch the inside wall. The reading on the vernier caliper or micrometer is the hose's inside diameter. For increased accuracy, it's recommended to take multiple measurements at different locations on the hose and average them.
How do you measure the length of a hydraulic hose?
To measure the length of a hydraulic hose, you need to identify a reference point on the hose assembly. This is usually measured from the end of the fitting or the center of the elbow.
Why is it important to match the hose to the fitting?
The correct sizing of hydraulic hoses and fittings requires consideration of factors such as fluid flow, pressure rating, temperature, and compatibility with system components. The size of a hydraulic hose is determined by its inner diameter, while fittings must match the hose size and thread specifications to ensure a secure, leak-free connection.
How do I correctly match hydraulic hoses and fittings?
Matching hydraulic hoses and fittings requires comprehensive consideration of key parameters such as pipe diameter, pressure, material, and thread type. Pipe diameter matching requires that the maximum fitting diameter be the same as or slightly larger than the hose's outer diameter (e.g., a DN10 hose with a DN12 fitting). A margin must be provided for the operating pressure (e.g., a 21 MPa hose with a 25 MPa fitting) to avoid the risk of bursting. Material selection must be tailored to the operating conditions (e.g., a polyurethane hose with a stainless steel fitting is corrosion-resistant, while a polyester hose with a carbon steel fitting is economical and practical). Thread types (BSPP/BSPT/NPT, etc.) must be consistent to ensure a tight seal. Special environments (high temperature/high pressure) require reinforced hoses and alloy fittings.
Can I use any fitting with any hose?
You cannot use any fitting with any hydraulic hose. The matching of hydraulic hoses and fittings must meet multiple requirements, including interface standards, pressure ratings, and sealing performance. Failure to do so can lead to seal failure, pressure leaks, and even equipment damage.
What happens if I use the wrong hose size?
A poor connection between hose and fitting due to mismatched sizes can result in pressure loss, contamination, and even equipment damage. In the hydraulic industry, hoses must be sized just right to ensure optimal performance, prevent leaks, and protect your equipment. Too small can result in restricted flow, leaks, and system damage; too large can lead to reduced performance and lost productivity. Therefore, ensuring the correct hose and fitting size is crucial.
So, the next time you're faced with a hose size selection dilemma, remember: size is crucial for hydraulic systems. Hydraulic hoses, fittings, and clamps must be the correct size to ensure proper operation. Choosing the right hose size depends on understanding the specific application and prioritizing safety and performance.
Sinopulse offers a comprehensive range of high-quality hoses, fittings, and expert advice to help you confidently meet your hydraulic challenges. Contact us today or leave a message below to let us guide you in finding the right hydraulic products!
Understanding the port size and operating pressure of each system component is crucial for selecting the right hose and fittings. We are a leading hydraulic hose manufacturer in China. If you are looking for the right-sized hydraulic hoses, hydraulic hose fittings, industrial hoses, and other hose-related products, please feel free to contact us. We always welcome you to contact us for more information on hose solutions that are right for your project.