In a hydraulic system, the return of working fluid rarely follows the exact same path it took when pressurized (such as in a simple hydraulic jack). More commonly, fluid is pumped through one line, completes its work, and then flows back to the reservoir through a separate suction and return hose. This is where hydraulic return hoses come into play.

Return hoses are made of rubber, also known as hydraulic oil return hoses. Return hoses are lower pressures than normal hydraulic hoses, and they must be resistance to oil and so they can transport types of hydraulic fluids and oil-based media. Their reinforcement layer is textile braids or fabric layers instead of steel wire reinforcement, and they combined with helical steel wire to make them more flexibility and stronger.
Selecting the right suction and return hoses is important for hydraulic system. These hoses transfer fluid between hydraulic components. In this guide, we discuss what hydraulic suction and return hoses are, their functions, and how to choose them.
What Is a Hydraulic Suction Hose?
A suction line connects the hydraulic reservoir to the pump, allowing fluid to flow smoothly into the pump. Its primary function is to ensure a continuous supply of hydraulic oil at low pressure, preventing interruptions that could lead to pump damage.
Key Considerations for Suction Hose
Suction hoses are made from synthetic rubber or thermoplastic materials. it is mainly used in hydraulic vacuum applications. The hose is flexible and durable. So they can prevent collapse when the pump draws fluid under suction.
The suction hose internal diameter should be large enough to work better. If the return hose ID is too small, it would restrict flow, leading to pump starvation, cavitation, and premature pump failure.
You should ensure that the return hose material is compatible with hydraulic fluid. If Incompatibility would make the hose swell, degrade, and reduce performance and cause the hydraulic system to break.
Suction hoses should have wide temperature range and vacuum levels of the hydraulic system. Before installation, you should ensure the hose’s rated temperature and pressure capabilities to ensure reliable performance under working conditions.
What Is a Hydraulic Return Hose?
A return hose transfers hydraulic fluid from hydraulic system components back to the reservoir. it is different from standard hydraulic hose, return hoses work under low pressure, but it should have high flow rates.
Key Considerations for Return Hoses
Return hoses size must be large enough to handle excessive back pressure from high fluid volumes . Choosing a hose with an adequate inside diameter ensures smooth flow and make system work efficiently, especially during peak flow conditions.
Return hoses withstand lower pressures compared to standard hydraulic hoses. But they should also operate according to the hydraulic system, because the hydraulic system is easy to pressure surges or fluctuations.
Return hoses are always exposed to challenging environmental conditions. Selecting abrasion-resistant covers and weather-resistant hoses can ensure long-term durability and reduced maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Suction and Return Hoses
Suction lines are used in vacuum and low pressure application, If you choose a low-quality hose, or use it beyond its rated pressure range, the hose may collapse.
Return lines are also used in low pressure environments, but they require a large flow rate and are oil resistant.
Both hoses are reinforced with textile braid, but the oil suction pipe is also reinforced with helical wire to prevent collapse
| Feature | Suction Hose | Return Hose |
| Function | Connects reservoir to pump; supplies oil to pump inlet | Carries oil back to reservoir after system operation |
| Operating Pressure | Operates under vacuum/low pressure | Operates under low pressure but must handle surges |
| Flow Characteristics | Must prevent collapse under suction | Must handle high flow rates without back pressure |
| Reinforcement Structure | Often reinforced with helical wire + textile layers | Typically textile braid or fabric layers; sometimes light wire helix |
| Key Risks | Cavitation, pump starvation, hose collapse, air ingress | Excessive back pressure, leakage, abrasion damage |
| Material Requirements | Oil-resistant, vacuum-resistant, flexible material | Oil-resistant, abrasion-resistant, weather-resistant cover |
| Typical Design Considerations | Large ID to minimize pressure drop; withstand vacuum | Sized for peak flow capacity; filtration recommended |
Functions of Hydraulic Suction and Return Hoses
In a hydraulic system, oil goes from the tank to the actuators, like hydraulic cylinders, to do the work. After that, the oil needs to go back to the tank. This way, the pump and other parts can keep running. The main job of the return line, such as in excavators, is to send the oil back to the tank. This keeps the oil moving and the system working.
2. Pressure Balancing
The return line also helps keep the pressure steady. When actuators work, the oil faces different pressure levels. To keep the system safe and stable, these pressures need to even out. The return line takes away extra pressure and keeps the system balanced. This makes the system run smoothly and dependably.
3. Heat Dissipation
When the system runs, the oil gets hot. If the oil gets too hot, the system becomes less efficient and parts wear out faster. By moving the oil back to the tank, the return line helps with cooling. The oil cools either in the tank itself or through a cooler. This keeps the temperature at the right level.
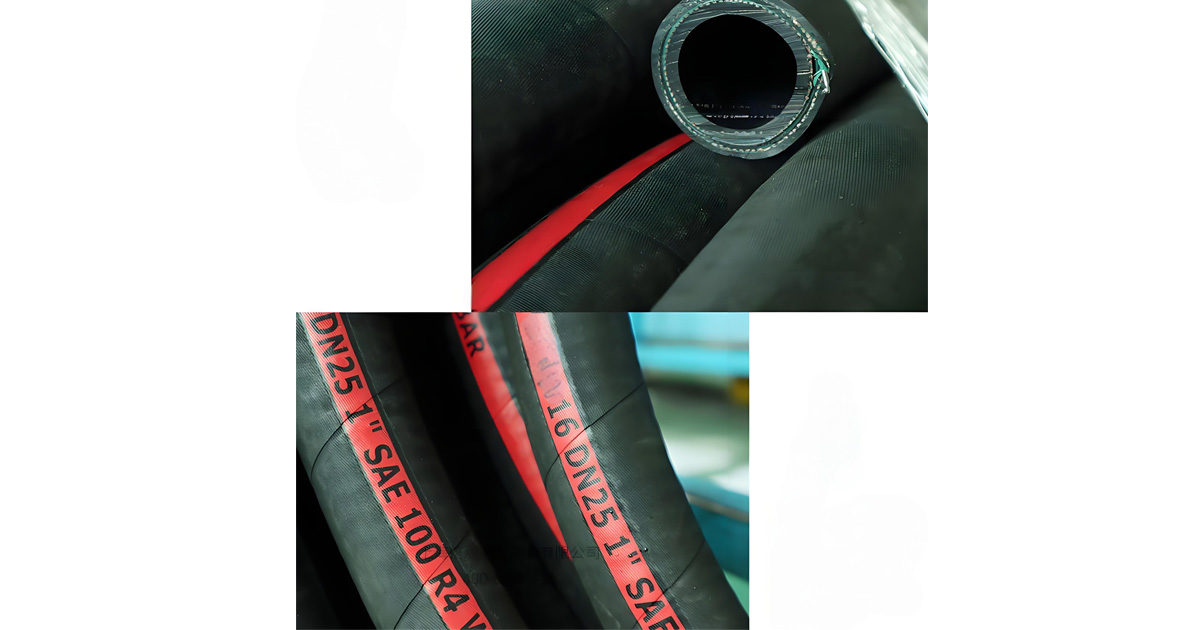

How to Determine the Right Hydraulic Suction and Return Hoses
Selecting the best suction and return hoses requires balancing system requirements, hose specifications, and operating conditions. Here is a step-by-step guide:
When you pick suction and return hoses, first check what the system needs. Look at the working pressure and the temperature. Measure the highest flow in the suction line and the return line. Think about the environment too. The hose may face heat, cold, abrasion, or chemicals.
Next, choose the right hose size. Match the inner diameter with the flow and pressure. In suction lines, keep the pressure drop low to avoid cavitation. In return lines, make sure the hose can handle peak flow without back pressure.
The hose material should match the fluid. you should use hoses used for petroleum oil, synthetic oil, or biodegradable oil.
SAE or ISO standard is basic standard to your suction and return hose. This makes the system safe and reliable.
Install the hose, you should use quality fittings and connectors to prevent leaks. Use clamps or brackets to fix the hose so it will not shake or rub.
| Step | Key Points |
| Understand System Requirements | - Identify working pressure and temperature - Measure maximum flow rate in suction and return lines - Evaluate environmental factors (heat, cold, chemicals) |
| Choose the Correct Hose Size | - Use hose ID charts to match flow rate & pressure - For suction lines: minimize pressure drop to prevent cavitation - For return lines: ensure capacity for peak flow without back pressure |
| Pay Attention to Compatibility | - Verify hose material compatibility with hydraulic fluid - Select hoses for petroleum-based, synthetic, or biodegradable oils |
| Check Certifications and Standards | - Ensure hoses comply with SAE or ISO standards - Reliability and safety depend on certified hoses |
| Consider Hose Assembly Requirements | - Use high-quality fittings/connectors to reduce leaks - Secure hoses with clamps/brackets to minimize vibration and wear |
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Suction and Return Hoses
Using hoses that are too small can cause problems. If the hose is a return line, the flow is restricted and this makes back pressure. Too much back pressure reduces upstream pressure. It can cause overheating, lower efficiency, and even damage parts.
If the hose is a suction line, a small size restricts flow at the pump inlet. This can create negative pressure or a vacuum. The pump may then cavitate. Cavitation can damage the pump, reduce system performance, and lower system pressure.
Not checking the pressure rating is also a risk. Suction and return hoses work at lower pressure than supply hoses, but if you go over their limit, they can fail or even burst.
Another mistake is ignoring filters. If you don’t install return-line filters, dirt and other contaminants keep moving through the system. This causes faster wear on parts and shortens the life of the hydraulic system.
Common Applications of Hydraulic Suction and Return Hoses
Hydraulic hoses are used to transfer fluids in hydraulic systems. Choose proper hose is important for hydraulic system work and hose lifetime. Here are some uses of suction and return hoses that can be used in fluid and system types.
Water-based hydraulic fluids are often used in fire resistance applications, like in mining or industrial. The hoses must resist water absorption and flexible in low temperatures.
In thermal fluid heating systems, the hoses carry very hot fluids. They must handle extreme heat without losing performance. These are often used in industrial heating or machines like plastic molding equipment.
For petroleum-based fluids, hoses need to resist oils and hydrocarbons. They are used in oil and gas work, transport, and storage. In these jobs, durability and fluid compatibility are important for safe use.
Some systems, like industrial presses or heavy mining machines, run under very high pressure. Hoses in these cases are reinforced to stop failures and to keep the system safe.
Transmission oil cooler lines use hoses that handle hot oil and help with cooling. This prevents overheating. You see them in cars and industrial machines where keeping the transmission safe is important.
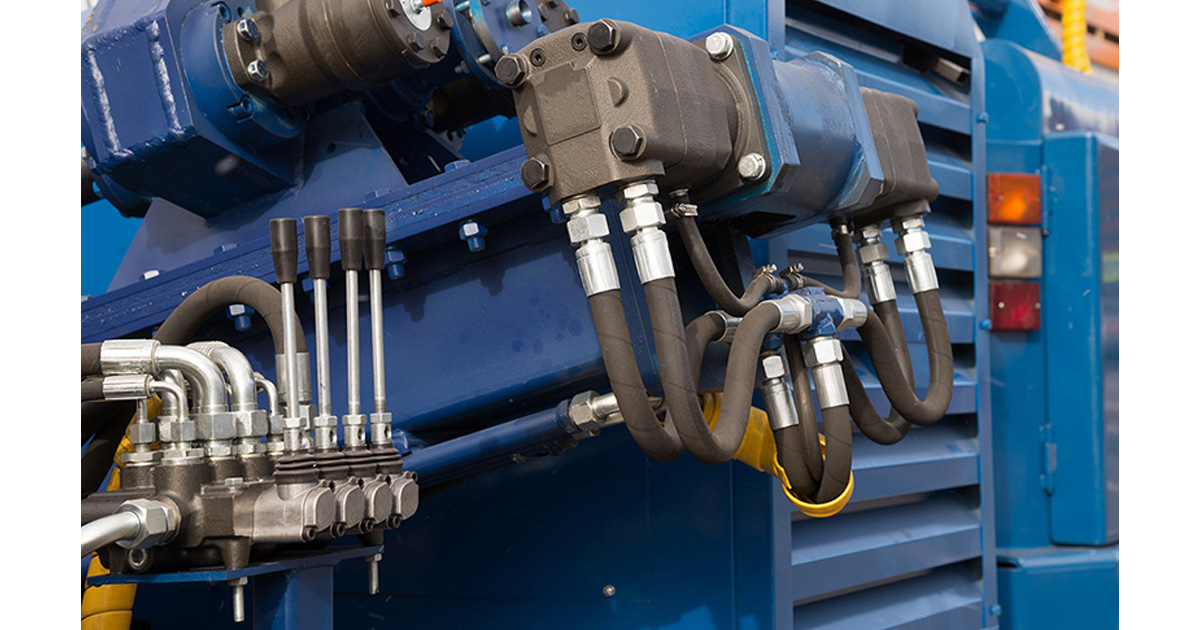
Select Sinopulse SAE 100R4 Suction and Return Hoses
This R4 hose combination meets a variety of suction and return application needs.
SAE 100R4 Suction and Return Line Construction
Inner Tube: Synthetic Rubber
Reinforcement: Multiple layers of fiber braid and one helical wire (the spiral withstands vacuum conditions up to 25 inches/Hg to prevent collapse).
Cover: Synthetic rubber, MSHA compliant
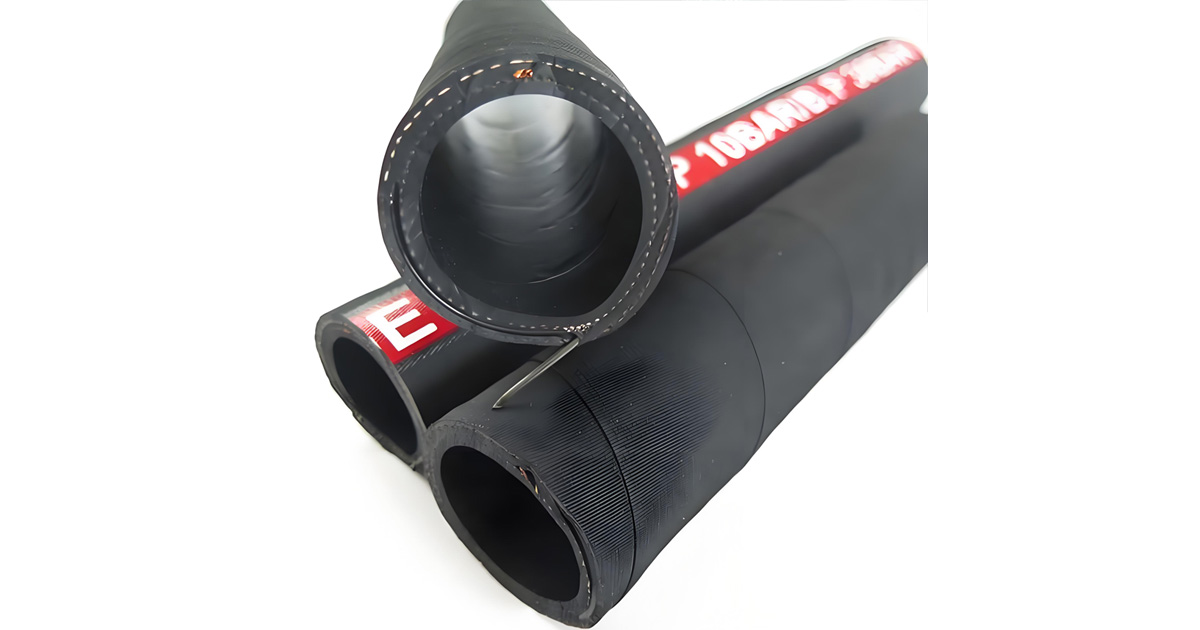

Features
Bend radius up to half the SAE minimum bend radius, suitable for standard and high-temperature applications, petroleum-based hydraulic fluids and lubricants
Meets or exceeds SAE 100R4 standard requirements
Interchangeable with Aeroquip FC318, Gates G4, Parker 881, and Weatherhead H039
Compatible with 188-24 - Hydraulic Suction and Return Lines Male NPTF valve stem, designed and engineered specifically for hydraulic suction line applications using SAE100R4 hydraulic hose. High-visibility laying line
Suitable for vacuum applications from 25 to 28 inches/Hg
Oil-resistant and weather-resistant synthetic rubber cover
811 petroleum-based hydraulic fluid with a high temperature range of -40°F to +257°F
Specification
| Code | Size | Inside Diameter | Outside Diameter | Working Pressure | Bursting Pressure | Bend Radius | Weight | Length | Ferrule & Fitting Code | |||||
| # | Dash | mm | Inch | mm | mm | bar | psi | bar | psi | mm | kgs/m | m | Codigo | Codigo |
| SNP-R412 | R4-12 | 19.1 | 3/4" | 19±0.4 | 34.4±0.4 | 21.0 | 305 | 63.0 | 914 | 120 | 0.990 | 60 | ××××1-××-12PO | / |
| SNP-R416 | R4-16 | 25.4 | 1" | 25±0.4 | 40.4±0.4 | 17.0 | 247 | 51.0 | 740 | 145 | 1.210 | 60 | ××××1-××-16PO | / |
| SNP-R420 | R4-20 | 31.8 | 1-1/4" | 32±0.4 | 49.0±0.4 | 14.0 | 203 | 42.0 | 609 | 195 | 1.680 | 60 | ××××1-××-20PO | / |
| SNP-R424 | R4-24 | 38.1 | 1-1/2" | 38±0.4 | 55.0±0.4 | 10.5 | 152 | 31.5 | 457 | 228 | 1.930 | 60 | ××××1-××-24PO | / |
| SNP-R432 | R4-32 | 50.8 | 2" | 51±0.4 | 68.0±0.4 | 7.0 | 102 | 21.0 | 305 | 300 | 2.470 | 60 | ××××1-××-32PO | / |
| SNP-R440 | R4-40 | 64.0 | 2-1/2" | 64±0.4 | 81.6±0.4 | 4.0 | 58 | 12.0 | 174 | 355 | 3.170 | 60 | ××××1-××-40PO | / |
| SNP-R448 | R4-48 | 76.0 | 3" | 76±0.4 | 94.4±0.4 | 4.0 | 58 | 12.0 | 174 | 455 | 4.030 | 60 | ××××1-××-48PO | / |
| SNP-R464 | R4-64 | 102.0 | 4" | 102±0.4 | 120.2±0.4 | 4.0 | 58 | 12.0 | 174 | 610 | 5.440 | 60 | ××××1-××-64PO | / |
Conclusion
Choosing the right hydraulic suction and return lines is improtant to hydraulic system. consider hose diameter, material, and pressure rating to ensure stable performance and a longer service life. Proper installation and regular maintenance can reduce machine downtime and make hoses more durable.
Need help?
Contact your Sinopulse sales representative or email us to speak with a member of our hose expert customer service team.