Ultimate Guide to Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius
Ever wonder why hydraulic hoses sometimes get damaged when they're bent too tightly? It all has to do with the hose's bend radius.
Bend radius is a critical factor in hydraulic system design and maintenance. Understanding how to calculate the minimum bend radius can ensure optimal hose performance and lifespan, preventing kinks and potential failures.
This blog post will guide you through the basics of hose bend radius and the simple process of calculating the minimum bend radius for hydraulic hoses. We'll break down the key factors involved and provide practical steps to ensure your hydraulic system operates safely and efficiently.
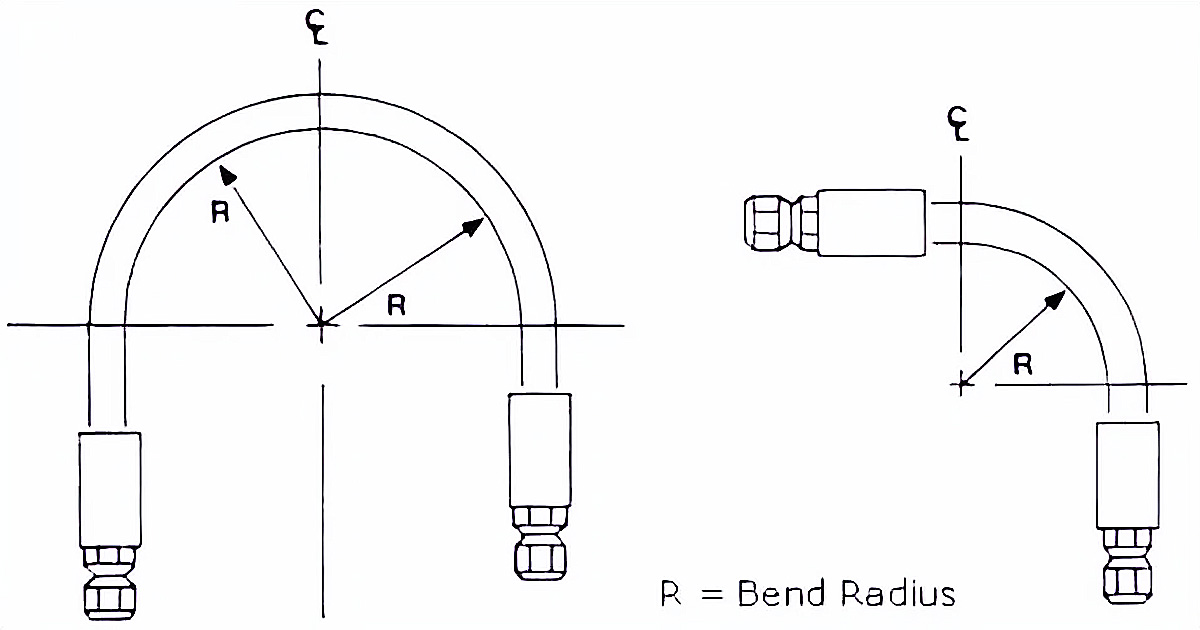
What Is Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius?
Bend radius is used to measure the internal curvature of a hydraulic hose. It is the minimum radius that can be bent into a pipe, tube, sheet, cable, or hose without kinking, damaging it, or shortening its life.
The bend radius of a hydraulic hose is the distance measured from the inner edge of the hose when the hose is bent 90°.
The bend radius of a hydraulic hose refers to the minimum diameter that a circular hydraulic hose can achieve. R stands for bend radius. The bend radius varies depending on the structure of the hydraulic hose, including the inner tube, reinforcement layer, and outer layer. The structure of the hydraulic hose can determine the bend radius of the hose.
Why Is Bend Radius Important for Hydraulic Hoses?
Correctly understanding the hose bending radius is crucial for hose installation. If the hose is too long, it will not only affect the appearance but also increase costs. If the hose is too short, when it is stretched or compressed under pressure, there is not enough room for expansion and contraction, which may also cause the hose to be damaged.
In addition, most hose failures are caused by improper installation of the hose assembly on the hydraulic system.
In most cases, the hose assembly is subjected to unacceptable torsional stress. A bend radius smaller than the requirements of the instructions and wear that causes corrosion of the reinforcement layer can also cause many failures.
The life of the twisted product will be significantly shortened, and it is easy to damage the hose or loosen the connection when under pressure.
Relevant tests show that twisting the hose by only 7° can reduce the service life of the hose by 80%. A bend radius that is too small will tear the reinforcing wire braid located on the outside of the bent part of the hose, significantly shortening the life of the product.
What Is the Minimum Bend Radius for Hydraulic Hoses?
The minimum bend radius of a hydraulic hose is the smallest diameter a ring-shaped hose can reach without damaging its internal structure or significantly shortening its service life.
This critical parameter is determined by the hose's construction (material, number of layers, reinforcement type), size, and pressure rating. Exceeding the minimum bend radius can lead to internal pressure stress, kink formation, reduced flow, and ultimately hose failure.
Key Considerations:
Hose Construction: Different types of hose (braided, spiral, thermoplastic) have different bend radii due to their different reinforcement layers. Spiral hoses generally have a larger minimum bend radius than braided hoses.
Hydraulic Hose Size: Larger hose diameters generally have larger minimum bend radii.
Pressure Rating: Higher-pressure hoses generally require a larger bend radius to prevent internal pressure stress.
Hydraulic Hose Application: The specific application and operating environment will affect the acceptable bend radius.
The Importance of Adhering to the Minimum Bend Radius:
Preventing Hose Failure: Exceeding the minimum bend radius can lead to internal pressure stress, resulting in leaks, ruptures, and potential injury or equipment damage.
Maintaining Flow: Sharp bends restrict fluid flow, reducing system efficiency and potentially damaging components. Extending Hose Life: Adhering to minimum bend radius requirements helps prevent premature wear and extend the life of hydraulic hoses.
Finding Minimum Bend Radius Information:
Manufacturer's Datasheet: The most reliable source is the manufacturer's datasheet for a specific hose type.
Industry Standards: Relevant industry standards and guidelines provide valuable information on minimum bend radius requirements.
By carefully considering minimum bend radius requirements and designing your hydraulic system accordingly, you can ensure optimal performance, safety, and longevity of your hydraulic system.
Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius Chart (with Sinopulse R1 hose Examples)
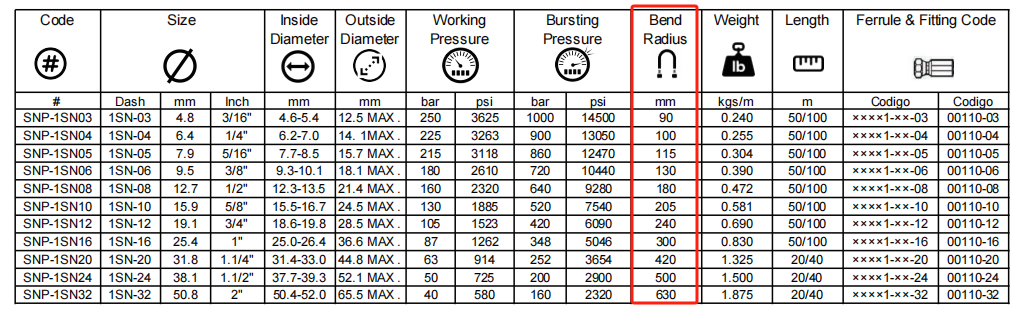
You can refer to a hydraulic hose bend radius chart to understand the bend capabilities of hydraulic hoses.
When selecting a hydraulic hose for your hydraulic system, always pay attention to the hose's bend radius. Exceeding the rated bend radius of a hydraulic hose can cause the hose to kink.
While specific bend radius values vary significantly depending on the hose's construction, material, pressure rating, and manufacturer, the following is an example of a general configuration for a bend radius chart. Always consult the manufacturer's datasheet for the specific specifications of the hose.
The following table provides an overview of the bend radius of hydraulic hoses.
| hose inner diameter(ID) | Minimum bend radius ratio example | Minimum bend radius example |
| 1/4 inch(0.25 inch) | 4:1 | 1 inch |
| 3/8 inch(0.375 inch) | 4:1 | 1.5 inch |
| 1/2 inch(0.5 inch) | 4:1 | 2 inch |
| 3/4 inch(0.75 inch) | 5:1 | 3.75 inch |
| 1 inch(1.0 inch) | 6:1 | 6 inch |
Notes:
Pressure: Higher operating pressures generally require a larger minimum bend radius. Manufacturers' charts typically indicate the hose's minimum bend radius at the maximum operating pressure.
Hose Construction: Different reinforcement types (e.g., wire braid, wire spiral, textile braid) will have different bend radius capabilities.
Dynamic vs. Static Applications: Hoses that are prone to flexing during operation may require a larger bend radius than those used in static applications. Manufacturers may provide a "dynamic bend radius" to account for this movement.
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the flexibility of the hose, thereby affecting the minimum bend radius.
Always refer to the manufacturer's specific data sheet for hydraulic hoses for accurate bend radius information. This table is for reference only.
Key Factors That Determine Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius
The inner tube, reinforcement layer, and outer layer increase the rigidity of the hydraulic hose. If the hydraulic hose is made of a rigid material, the bend radius will be very small. The reinforcement layer of the hydraulic hose can modify the bend radius. A smaller bend radius makes the hydraulic hose more flexible. The more reinforcement layers, the greater the rigidity of the hydraulic hose, but also the greater the difficulty in bending.
Due to the reinforcement structure of the hydraulic hose, braided hydraulic hose is more flexible than spiral hydraulic hose. This also accounts for the different bend radii of hydraulic hoses. The number of stainless steel wire layers also affects the bend radius.
Before installing the hydraulic hose, carefully consider the specifications of the hydraulic hose, including the hose length and bend radius. When installing the hydraulic hose, the bend radius must not be less than the minimum bend radius, otherwise it may cause the hydraulic hose to break, leak, or fold.
Bend Radius for Different Hose Types (1SN, 2SN, 4SP, etc.)
1SN Bend Radius: 90-630mm
2SN Bend Radius: 90-630mm
4SP Bend Radius: 180 - 660mm
How to Calculate Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius
How to determine the shallowest bend a hydraulic hose can withstand.
Determining the Hose Diameter
First, you need to know the inside diameter (ID) of the hydraulic hose. This measurement is usually printed directly on the hose. Look for a number followed by an inch symbol (") or a millimeter symbol (mm). This diameter is the basis for calculating the minimum bend radius.
Determining the Minimum Bend Radius Ratio
Next, you need to find the minimum bend radius ratio for your specific hose type. This ratio is usually provided by the hose manufacturer in their product specifications or datasheets. It is usually expressed as a multiple of the hose's inside diameter (for example, 4:1). Different hose constructions and materials will have different bend radius ratios, so always consult the manufacturer's information.
Performing the Calculation
Once you have determined the hose's inside diameter and minimum bend radius ratio, the calculation is simple. Simply multiply the hose's inside diameter by the minimum bend radius ratio. For example, if the hose has a 1-inch inside diameter and a 4:1 minimum bend radius ratio, the minimum bend radius is 1 inch * 4 = 4 inches. This calculated value represents the minimum radius the hose should be bent to avoid damage and ensure optimal performance.
How to Measure the Bend Radius of an Installed Hose
The specific steps are as follows:
Determine the hose centerline: Find the centerline of the hose bend. This can usually be done by drawing two parallel lines on the outside and inside of the bend and then finding the center point between these two lines.
Measure the length of the bend: Measure the length of the hose bend from the start to the end of the bend.
Measure the bend angle: Measure the angle of the bend. If it is a complete semicircle, the angle is 180 degrees.
Calculate the bend radius: Use the following formula:
L = A/360° x 2πr, where L is the length of the bend, A is the bend angle, and r is the bend radius.
Solving this formula, you can calculate r, which is the bend radius of the hose.
Other methods:
Direct measurement:
If the hose bend is free to move, you can try using a tape measure or other measuring tool to directly measure the radius of the outside of the bend, but this is generally less accurate.
Use specialized tools:
For more complex bends, you can use specialized bend radius measuring tools or methods such as laser scanning to obtain more accurate data.
Hose Material:
Different hose materials have different minimum bend radii. Please refer to the manufacturer's technical specifications.
Hose Diameter:
The hose's diameter also affects the bend radius. Generally speaking, larger diameters increase the minimum bend radius.
Avoid Excessive Bending:
Excessive bending can shorten the hose's lifespan or even cause it to rupture. Therefore, during installation and use, avoid exceeding the hose's minimum bend radius.
Common Mistakes in Hydraulic Hose Routing
Common errors in hydraulic hose routing include improper fitting installation, hose kinking, wear and tear, aging, and friction with surrounding objects. These issues can lead to oil leaks, bursts, and performance degradation. Improper installation: Loose fittings and aged or damaged seals can lead to oil leaks.
1. Fitting problems
Thread damage: Damage to threads during installation can cause leaks in joints.
Overtightening: Overtightening fittings can damage threads or hoses, leading to oil leaks or bursts.
2. Hose Problems:
Kinking:
Hoses can easily kink when bent or subjected to uneven loads, affecting the proper functioning of the hydraulic system and even causing a burst.
Abrasion:
Hoses can rub and squeeze against surrounding objects, causing wear on the outer layer, reducing their pressure-bearing capacity and even causing a burst.
Aging:
Hose material ages and loses its elasticity due to prolonged use or exposure to harsh environments, making them susceptible to cracking or bursting.
Insufficient or excessive length:
Hoses that are too short may stretch, while hoses that are too long are prone to tangling and kinking. 3. Other Common Mistakes:
Failure to Consider the Hose Bend Radius:
A bend radius that is too small can easily cause the hose to overbend, increasing stress and even bursting.
Failure to Consider the Operating Pressure:
The selected hose may not have sufficient pressure-bearing capacity and may burst under high-pressure conditions.
Failure to Consider Environmental Factors:
High temperatures, low temperatures, and chemical corrosion can accelerate hose aging and damage.
Failure to Perform Regular Inspections:
Failure to perform regular inspections and maintenance can prevent problems from being discovered and resolved promptly.
Failure to Consider the Clearance Between the Hose and Surrounding Objects:
Insufficient clearance between the hose and surrounding objects can easily cause friction, leading to wear or damage.
Preventative Measures:
Select appropriate hoses and fittings, ensuring their quality and pressure-bearing capacity meet the requirements.
Install the hose correctly, ensuring fittings are secure and seals are intact.
Avoid kinking and excessive bending of the hose, and maintain a reasonable bend radius.
Prevent the hose from rubbing or squeezing against surrounding objects.
Inspect the hose and fittings regularly to identify and resolve any problems promptly.
For harsh environments, choose hoses with good corrosion and temperature resistance. During installation and maintenance, follow relevant safety regulations and operating instructions.
Tips to Prevent Hydraulic Hose Failure Due to Improper Bending
Bend radius is one aspect of hydraulic hose assembly that requires careful consideration. Calculating the bend radius is essential to prevent hydraulic hose failure.
The following are various causes of hydraulic hose damage that can lead to leaks or breakage. Overly tight hose routing and improper bend radius can cause excessive stretching. Excessively bent hoses can lead to hydraulic fluid leaks, loosening of fittings, and other problems.
Failure to adhere to hydraulic hose specifications and exceeding the bend radius can restrict the flow of fluid within the hose and cause excessive heating due to the added friction of improper hose assembly.
Overbending a hydraulic hose, ignoring the minimum bend radius indicated on the hose jacket, can result in a poor installation. Always check the bend radius of the hydraulic hose before installation.
For more detailed information on our hydraulic hose bend radius options, please feel free to contact us.
Best Practices for Hose Routing and Installation
Determining the Required Hydraulic Hose Size
The first step is to determine the hydraulic hose size required for your project. You must understand the appropriate measures for each component. You can refer to a hydraulic hose size chart and correlate the sizes with your hydraulic system. Typical hydraulic hoses come in a variety of sizes. This chart highlights the manufacturer, standard, and diameter of the hydraulic hose. Some hydraulic hose size charts may include operating pressure, production date, and other information.
You should also identify the appropriate supporting equipment for these hydraulic hose sizes. For example, hydraulic hose fittings, support clamps, and protective covers are important considerations. For hydraulic hose fittings, you can refer to the hydraulic fitting size chart.
Avoiding Twisting Hose Assemblies
Twisting hose assemblies is a common mistake that can harm system performance. Improper installation can cause hose assemblies to twist. Additionally, some applications may involve torsional stress or excessive rotational forces. In these cases, twisted hose assemblies may occur. Twisting hose assemblies can cause specific problems, such as reduced flow and increased wear.
To avoid hose twisting, carefully plan the hose routing. Consider the shortest, straightest path with the fewest bends and twists. You can also use support devices and clamps to secure them in place. However, you can also contact our customer service for assistance. Our dedicated team is waiting to respond to your inquiries.
Avoid Overbending Hoses
Overbending hoses is another mistake that can affect hydraulic system performance. Hydraulic hoses are designed to transfer fluids under high pressure. They help accommodate necessary movement. Overbending and tight-radius bends can affect the hydraulic hose and the entire system. Therefore, avoiding overbending hoses is crucial to ensuring proper hydraulic hose routing.
Each hydraulic hose has a specified minimum bend radius recommended by the manufacturer. Be sure to follow these instructions to avoid kinks and damage. The minimum bend radius is the smallest radius within which the hydraulic hose can operate smoothly. Additionally, carefully plan the hose routing before installation. Avoid sharp bends and angles.
Using Hose Elbows or Hose Adapters
Using hose elbows or hose adapters is a useful technique for hydraulic hose routing. They allow for changes in direction and connections without distorting the hydraulic line. Hose elbows, also known as hose bends, come in various angles, such as 45, 60, or 90 degrees. Custom hose elbows are also available for your application. Hose adapters, on the other hand, connect different types of hoses to fittings or other equipment. Hose adapters also come in a variety of configurations and sizes, serving a variety of uses.
Hose elbows and adapters play a crucial role when navigating obstacles or around corners. Choose the correct type that matches the specifications and sizes of the hoses and fittings you are using. You can also refer to the manufacturer's guidelines for more information.
Using Appropriate Hydraulic Hose Fittings
We strongly recommend not mixing hydraulic fittings and hoses during installation. As a first step, you've already checked the sizes of your hydraulic hoses and fittings. Therefore, during installation, follow your plan and use the appropriately sized hoses. Please note that the hose fittings you choose must match the diameter of your hydraulic hose.
We recommend choosing hydraulic hose fittings from the same manufacturer. Choosing the same brand ensures a reliable hydraulic hose installation and provides a safe and qualified hydraulic system. However, please consult our experts for more information on hydraulic hose standards and sizes. You can share your design layout with them and receive recommendations for the best options for your project.
Using Hydraulic Hose Clamps
Hose clamps secure and fasten hydraulic hoses to fittings, pipes, or other system components. Hydraulic line clamps prevent hose movement, leaks, and damage. By preventing these obstructions, they maintain the safety and efficiency of your hydraulic system. Therefore, hydraulic hose clamps are essential components for hydraulic routing.
Choose the correct hydraulic hose clamp based on size, material, and application. There are many different types of clamps available. For example, worm gear clamps, T-bolt clamps, and spring clamps are worth noting. The choice depends on the type of hydraulic system and the application. Furthermore, you can position the hose clamp at a certain distance from the hose end and fitting. This ensures a secure grip. Please follow the manufacturer's guidelines or contact our customer support team for more information.
Using Hydraulic Hose Support Clamps
The difference between hose clamps and hose support clamps is simple. They each serve different purposes in hydraulic and fluid transfer systems. Hose clamps typically secure hydraulic hoses to fittings, pipes, or other components. Hydraulic hose support clamps, on the other hand, are designed to support and organize hoses, cables, or lines. These support clamps do not secure hoses to fittings.
Hydraulic hose clamps are also crucial for organizing and securing hydraulic hose routing. They attach the hose to the surface and prevent it from sagging and tangling, thus maintaining an orderly arrangement. Therefore, choosing the right type of hydraulic hose support clamp is essential.
Avoid Full Extension of Hose Assemblies
When a hydraulic system is operating, pressurized fluid slightly shortens the hose length, thus expanding the hose diameter. Therefore, allowing a hydraulic hose assembly to be fully extended can have adverse consequences. This repetitive stress can force the hose out of the fitting under pressure. It can also significantly shorten the hose's service life. Ultimately, it can lead to potentially catastrophic failure. Therefore, preventing hose assemblies from fully extending is crucial to maintaining service life.
To prevent this problem, you can incorporate slight bends or slack into your hose routing design. Note that excessive bends can also cause problems. Therefore, consult a professional to assist you in designing the proper bend radius.
Using Hydraulic Hose Protective Equipment
One of the best practices for properly routing hydraulic hoses is using a hydraulic hose protector. Hydraulic hose spiral wrap offers a wide range of benefits. First, it protects the hydraulic hose from abrasion, shock, heat, and chemicals. Second, it increases the service life of the hydraulic hose. It also ensures safety by preventing leaks, explosions, and unexpected failures. Overall, it plays a vital role in maintaining the overall efficiency of the hydraulic system.
For more information on hydraulic hose spiral wraps, you can read our blog post. "Hydraulic Hose Spiraling – The Ultimate Guide" explains all the fundamentals. Therefore, choosing the right hydraulic hose protector is crucial for better routing.
Cleaning Hydraulic Hose Routing
Finally, the last and most important practice you should perform is regular cleaning of hydraulic hose routes. Cleanliness here means reducing unnecessary lengths of hydraulic hoses. You can use hose elbows and adapters to save space for regular maintenance. Using this equipment helps to clean up routing. Ultimately, it extends the life of the hydraulic hoses. It also makes regular maintenance easier.
In fact, regular maintenance can improve the overall performance of your hydraulic system. It helps prevent blockages, contamination, and damage that can lead to costly repairs. During maintenance, don't forget to depressurize and shut down the hydraulic system. Then, blow compressed air through the routes to remove loose contaminants. Afterwards, flush with compatible hydraulic fluid to remove internal impurities. Inspect and check for leaks or damage. Finally, reassemble and test the entire system.
Bend Radius vs. Hose Flexibility: What’s the Difference?
Bend radius and hose flexibility are two different concepts, but they are closely related. The bend radius refers to the minimum radius a hose can reach when bent, while flexibility refers to its ability to resist bending and recover its shape after bending.
The bend radius primarily describes the degree to which a hose can bend, while flexibility describes its ability to resist bending and recover.
The bend radius is a specific parameter of a hose, while flexibility is a performance indicator.
When selecting a hose, it is important to consider both the appropriate bend radius and the hose's flexibility based on the actual application requirements.
Conclusion: Why Bend Radius Matters in Hydraulic System Design
Determining the correct bend radius for hydraulic hoses is crucial for achieving optimal system performance, safety, and longevity. By carefully considering factors such as hose construction, size, pressure rating, and application, and consulting manufacturer datasheets and industry standards, you can ensure proper hose installation and operation.
For high-quality hydraulic hoses that meet the most stringent industry standards, consider Kingdaflex. We offer a wide variety of wholesale hydraulic hoses designed for demanding applications. Contact us today to learn more about our products and discuss your specific needs.
faq
Bend Radius Standards for Common Hydraulic Rubber Hoses
Wire braided hydraulic rubber hoses: For single-layer steel wire braids, the bend radius is generally 6 times the outer diameter; for double-layer steel wire braids, the bend radius is 7 times the outer diameter; and for triple-layer steel wire braids, the bend radius is 8 times the outer diameter. For example, a single-layer steel wire braided rubber hose with an outer diameter of 10mm has a minimum bend radius of 60mm.
Wire-wound hydraulic rubber hoses: For medium-pressure steel wire-wound rubber hoses, the bend radius is generally 9 times the outer diameter; for high-pressure steel wire-wound rubber hoses, the bend radius is 10-12 times the outer diameter.
How to Determine the Required Bending Radius
Review the product manual and the manufacturer's technical specifications as the most important basis. Calculate the bending radius using a formula (some standards provide relevant formulas) that takes into account factors such as pipe diameter and pressure. Also, consult actual application cases and draw on empirical data from similar operating conditions.
How to Measure the Required Bend Radius of Hydraulic Hose
During rubber hose production, a dedicated bend radius measurement mold is used to align the hose with the mold after bending. At the construction site, a tape measure is used to measure the arc length of the bend and calculate the bend radius based on the central angle. Laser measurement equipment is used to non-contactly measure the hose's bend profile and accurately calculate the bend radius.
How to Install with a Proper Bend Radius
Before installation, determine the proper route based on design requirements and ensure sufficient space to achieve the specified bend radius. Avoid forcing the hose to bend. Use appropriate elbows, fittings, and other connectors to reduce unnecessary bending. Install fixtures at bends to prevent movement during operation and changes in the bend radius.
How to Maintain a Proper Bend Radius
Regularly inspect the hose's bends for wear, deformation, cracks, and other abnormalities. If the bend radius changes due to external factors, adjust it promptly. Pay attention to the operating temperature to avoid excessively high or low temperatures that may affect the hose's flexibility and bending properties.
Where are the different bend radii for wire-wound hydraulic rubber hoses used?
Medium-pressure applications: The recommended bend radius is 9 times the outer diameter, balancing pressure-bearing stability and pipe bending deformation capacity.
High-pressure requirements: The bend radius should be extended to 10 to 12 times the outer diameter to ensure that high-pressure fluid transmission does not cause structural damage or fatigue fracture.
What is the relationship between the number of reinforcement layers in braided hydraulic hoses and the bend radius?
Single-layer steel wire braid: The recommended minimum bend radius is 6 times the outer diameter of the hose (e.g., for a 10mm outer diameter, the safe bend radius should be ≥ 60mm).
Two-layer steel wire braid: The bend radius should be increased to 7 times the outer diameter to accommodate increased compressive and tensile strength requirements.
Three-layer high-strength braid: The bend radius is increased to 8 times the outer diameter, balancing the rigidity of the multi-layer structure with the limitations on flexibility.